 Despite the fact that the writer chose to use the outdated and slightly offensive term “masseur,” this is a very informative article.
Despite the fact that the writer chose to use the outdated and slightly offensive term “masseur,” this is a very informative article.
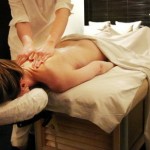
According to this recent article from the Well section of the NYTimes, researchers found that massage reduced the production of compounds called cytokines, which play a critical role in inflammation. Massage also stimulated mitochondria, the tiny powerhouses inside cells that convert glucose into the energy essential for cell function and repair. âThe bottom line is that there appears to be a suppression of pathways in inflammation and an increase in mitochondrial biogenesis,â helping the muscle adapt to the demands of increased exercise, said the senior author, Dr. Mark A. Tarnopolsky.
Many people pop an aspirin or Aleve at the first sign of muscle soreness, but Dr. Tarnopolsky suggests that, in the long run, a professional massage may even be a better bargain than a pill. âIf someone says âThis is free and it might make you feel better, but it may slow down your recovery, do you still want it?â he asked.
âThis is important research, because it is the first to show that massage can reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines which may be involved in pain,â said Tiffany Field, director of the Touch Research Institute at the University of Miami Medical School. She was not involved in the study. âWe have known from many studies that pain can be reduced by massage based on self-report, but this is the first demonstration that the pain-related pro-inflammatory cytokines can be reduced.â she said.
![[Home]](http://www.feelintegrated.com/images/logo.gif)
